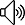本文實(shí)例講述了Python使用sklearn實(shí)現(xiàn)的各種回歸算法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
使用sklearn做各種回歸
基本回歸:線性、決策樹、SVM、KNN
集成方法:隨機(jī)森林、Adaboost、GradientBoosting、Bagging、ExtraTrees
1. 數(shù)據(jù)準(zhǔn)備
為了實(shí)驗(yàn)用,我自己寫了一個(gè)二元函數(shù),y=0.5*np.sin(x1)+ 0.5*np.cos(x2)+0.1*x1+3。其中x1的取值范圍是0~50,x2的取值范圍是-10~10,x1和x2的訓(xùn)練集一共有500個(gè),測(cè)試集有100個(gè)。其中,在訓(xùn)練集的上加了一個(gè)-0.5~0.5的噪聲。生成函數(shù)的代碼如下:
def f(x1, x2):
y = 0.5 * np.sin(x1) + 0.5 * np.cos(x2) + 0.1 * x1 + 3
return y
def load_data():
x1_train = np.linspace(0,50,500)
x2_train = np.linspace(-10,10,500)
data_train = np.array([[x1,x2,f(x1,x2) + (np.random.random(1)-0.5)] for x1,x2 in zip(x1_train, x2_train)])
x1_test = np.linspace(0,50,100)+ 0.5 * np.random.random(100)
x2_test = np.linspace(-10,10,100) + 0.02 * np.random.random(100)
data_test = np.array([[x1,x2,f(x1,x2)] for x1,x2 in zip(x1_test, x2_test)])
return data_train, data_test
其中訓(xùn)練集(y上加有-0.5~0.5的隨機(jī)噪聲)和測(cè)試集(沒有噪聲)的圖像如下:
2. scikit-learn的簡(jiǎn)單使用
scikit-learn非常簡(jiǎn)單,只需實(shí)例化一個(gè)算法對(duì)象,然后調(diào)用fit()函數(shù)就可以了,fit之后,就可以使用
predict()
函數(shù)來預(yù)測(cè)了,然后可以使用
score()
函數(shù)來評(píng)估預(yù)測(cè)值和真實(shí)值的差異,函數(shù)返回一個(gè)得分。
完整程式化代碼為:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
###########1.數(shù)據(jù)生成部分##########
def f(x1, x2):
y = 0.5 * np.sin(x1) + 0.5 * np.cos(x2) + 3 + 0.1 * x1
return y
def load_data():
x1_train = np.linspace(0,50,500)
x2_train = np.linspace(-10,10,500)
data_train = np.array([[x1,x2,f(x1,x2) + (np.random.random(1)-0.5)] for x1,x2 in zip(x1_train, x2_train)])
x1_test = np.linspace(0,50,100)+ 0.5 * np.random.random(100)
x2_test = np.linspace(-10,10,100) + 0.02 * np.random.random(100)
data_test = np.array([[x1,x2,f(x1,x2)] for x1,x2 in zip(x1_test, x2_test)])
return data_train, data_test
train, test = load_data()
x_train, y_train = train[:,:2], train[:,2] #數(shù)據(jù)前兩列是x1,x2 第三列是y,這里的y有隨機(jī)噪聲
x_test ,y_test = test[:,:2], test[:,2] # 同上,不過這里的y沒有噪聲
###########2.回歸部分##########
def try_different_method(model):
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
score = model.score(x_test, y_test)
result = model.predict(x_test)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(len(result)), y_test,'go-',label='true value')
plt.plot(np.arange(len(result)),result,'ro-',label='predict value')
plt.title('score: %f'%score)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
###########3.具體方法選擇##########
####3.1決策樹回歸####
from sklearn import tree
model_DecisionTreeRegressor = tree.DecisionTreeRegressor()
####3.2線性回歸####
from sklearn import linear_model
model_LinearRegression = linear_model.LinearRegression()
####3.3SVM回歸####
from sklearn import svm
model_SVR = svm.SVR()
####3.4KNN回歸####
from sklearn import neighbors
model_KNeighborsRegressor = neighbors.KNeighborsRegressor()
####3.5隨機(jī)森林回歸####
from sklearn import ensemble
model_RandomForestRegressor = ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=20)#這里使用20個(gè)決策樹
####3.6Adaboost回歸####
from sklearn import ensemble
model_AdaBoostRegressor = ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor(n_estimators=50)#這里使用50個(gè)決策樹
####3.7GBRT回歸####
from sklearn import ensemble
model_GradientBoostingRegressor = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=100)#這里使用100個(gè)決策樹
####3.8Bagging回歸####
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor
model_BaggingRegressor = BaggingRegressor()
####3.9ExtraTree極端隨機(jī)樹回歸####
from sklearn.tree import ExtraTreeRegressor
model_ExtraTreeRegressor = ExtraTreeRegressor()
###########4.具體方法調(diào)用部分##########
try_different_method(model_DecisionTreeRegressor)
3.結(jié)果展示
更多關(guān)于Python相關(guān)內(nèi)容感興趣的讀者可查看本站專題:《Python數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)與算法教程》、《Python加密解密算法與技巧總結(jié)》、《Python編碼操作技巧總結(jié)》、《Python函數(shù)使用技巧總結(jié)》、《Python字符串操作技巧匯總》及《Python入門與進(jìn)階經(jīng)典教程》
希望本文所述對(duì)大家Python程序設(shè)計(jì)有所幫助。
更多文章、技術(shù)交流、商務(wù)合作、聯(lián)系博主
微信掃碼或搜索:z360901061

微信掃一掃加我為好友
QQ號(hào)聯(lián)系: 360901061
您的支持是博主寫作最大的動(dòng)力,如果您喜歡我的文章,感覺我的文章對(duì)您有幫助,請(qǐng)用微信掃描下面二維碼支持博主2元、5元、10元、20元等您想捐的金額吧,狠狠點(diǎn)擊下面給點(diǎn)支持吧,站長非常感激您!手機(jī)微信長按不能支付解決辦法:請(qǐng)將微信支付二維碼保存到相冊(cè),切換到微信,然后點(diǎn)擊微信右上角掃一掃功能,選擇支付二維碼完成支付。
【本文對(duì)您有幫助就好】元