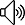英文全文:
http://mediaproducts.gartner.com/reprints/bea/vol1/article2/article2.html
?
?
純粹只玩BPM的廠商繼續占據領先位置,但“經典”BPMS的應用場景已由應用基礎設施變化為模型驅動的、整合的環境。
?
魔力象限圖:
?
從產品角度,評估BPM廠商的10項標準。
-
流程執行與狀態管理引擎:
Process execution and state management engine: This orchestrates the sequence of multiple process interaction patterns and maintains the state of process instances, activities and steps among humans and systems based on the metadata and process flow that were modeled. Supporting H2H, H2S and S2S interactions, case management and compensating transactions. -
模型驅動的設計和開發環境:
Model-driven design/development environment: This is a drag-and-drop modeling environment that includes process wizards, templates and "what you see is what you get" development tools to model and architect all process artifacts, including process design, human interaction, rule interaction, user interface, system interaction and electronic forms. Features such as search, version management, repository partitioning, publish and subscribe services, and check-in/check-out. -
文檔與內容管理:
Document and content management: This is document and records management technology that is capable of storing, archiving, indexing, picking and tracking all types of content (for example, structured and unstructured data) inside and outside the context of a process flow. Features include folder management, document and image indexing, management of structured and unstructured data, and document archiving, as well as document security management. -
用戶協同:
User and group collaboration: These are design time and runtime human teamwork tools. The design time collaboration tools provide development tools for business users and IT to help close the communication gap between the two groups. Runtime tools provide work collaboration facilities so that work teams can drive work to completion faster and can detect, suggest and change system behavior for optimal system performance. This area includes shared work queues, project portals/rooms, role-based development, instant messaging/blogs and community bulletin boards. -
流程組件注冊與倉庫:
Process component registry/repository: This stores all process definitions, components, models, rules and other process data that can be browsed by humans and called by systems. It supports search, version management, repository partitioning, publish and subscribe services, and check-in/check-out of all software components created and orchestrated at runtime. -
系統管理與維護:
System management and administration: These tools set up and maintain system and human access, as well as provide monitoring tools to govern the health of running systems. They include role management, security management, system management monitoring, LDAP integration and Active Directory deployment tools. -
業務規則管理:
Business rule management: The ability to abstract and execute business policies and decisions/rules from the underlying application and to enable more-flexible process change. This includes event-based rules, inference-based rules, rule test and debugging, rule simulation/what-if analysis and rule templates. -
在線與離線的仿真與優化:
In-line and offline simulation and optimization: These are process simulation and optimization tools that use real-time, historical and estimated data values to detect and suggest process optimization opportunities. Simulation tools should have tight integration with the development environment to enable round-trip engineering. This functional area supports predictive analysis (financial and risk), concurrent process and rule simulation, a simulation repository, optimization algorithms and round-trip engineering. -
流程事件管理:
Business event management, business activity monitoring (BAM) and business intelligence (BI) management: Business monitoring and reporting tools are used for governing and alerting business managers on current and changing business operation behaviors. Features include event listeners, alarms, triggers of online analytical processing/BI reporting, key performance indicator dashboards, graphical process monitoring and process discovery tools. -
系統連接性:
System connectivity: These tools enable system architects to publish and subscribe system services, choreograph service interaction and set up bidirectional connections to various, back-end business applications via prepackaged system connectors, such as Enterprise JavaBeans or SOAP, technical adapters, service support, enterprise service bus, data transformation tools and application adapters.
?
個人感受:翻閱了這10條技術標準,一個產品之所以只能成為工作流(Workflow),而不是業務流程管理(BPM),是因為工作流只具備了流程執行引擎、模型設計等基本工具,而在與流程相復合的功能,如上面提到的文檔管理、業務規則管理、事件管理/BI/BAM/DashBoard、流程模擬與優化以及流程運維管理做的不夠深入。
但有意思的是,似乎先進的BPM產品所具備的業務層次上的BPM能力超越了目前國內業務應用現狀,很多信息化建設還僅僅處于起步狀態,這些信息化建設在初始階段往往只需要一個工作流引擎即可。
加上本地化因素、市場因素、國外產品難以導入等,造成BPM產品在國內曲高和寡(高端應用除外!)。
?
?
BEA ALBPM
優勢:- 可以讓業務人員參與到IT構建中,參與到業務流程的全生命周期;
- 開放的標準,較強的H2H,H2S,S2S功能;
- 在將支持業務人員參與到流程驅動的解決方案,包含SOA與WEB2.0
- 與Weblogic產品未完全整合,如與Weblogic Integration的整合,包括文檔、管理;
- BPM價值主要基于產品的創新,可能難于與追求商業結果的BPM購買者形成共鳴;
- 僅支持設計時的仿真和優化。。??
IBM
優勢:- 整合所有資源推動客戶接受BPM,這些資源包括全球服務、大學推廣、業務咨詢以及合作伙伴生態系統;
- 擁有廣泛的、強勢的BPM-enabling技術,幫助客戶做大作強SOAs,并達到BPM級別;
- 有提供給業務人員和分析師的工具Business Modeler、Business Monitor,支持在設計、監控、分析等階段的流程改進;
- 已圍繞SOA構建了卓有成效的軟件和IT服務生態系統,對SOA與BPM的市場有很強的預見性。
- 不只是一個BPM產品,BPM戰略包括很廣泛的產品線,包括Tivoli、Webshpere、Lotus、FileNet和Rational。參與BPM改進生命周期的角色不能形成統一的產品體驗;
- 改變已部署執行的流程依然需要IT人員支配;
- BPMS產品和專業服務不支持business-user-driven,不具備敏捷開發的特征。
Oracle
優勢:- 用戶可以漸進的增強BPM能力,如可從Oracle BPA套件起步,然后增加使用BPEL Process Manager和Oracle BAM;
- Oracle BPA套件和SOA套件使用同一套元數據(Process Blueprint),支持業務人員和開發人員在設計時協作;在BPA套件設計的流程保存為BPMN格式,通過Process Blueprint可轉化為BPEL格式;Oracle JDeveloper可以編輯這些模型。這樣可形成閉環管理,盡管是人工進行;
- BPEL Process Manager有很強的人工流程管理功能,如投票、組分配和時間期限等;
- Oracle事件驅動型的BAM較強,可以可視化的輕松創建內置的度量指標和儀表盤(盡管需要有很強的數據理解能力)
- 由于根據不同角色而定的的設計和開發環境,不同角色的業務人員和開發人員的交流將受限。例如,跨角色的模型交流需要從不同的工具中集中版本;
- 總體的用戶體驗為傳統的開發方法論,而不是模型驅動、協作和敏捷的方法;
- 模擬功能只能使用BPA套件在設計階段支持。
Tibco
優勢:- Business Studio2.0是一個基于Eclipse的統一開發環境,支持由業務分析師和開發人員使用。適應BPEL2.0標準,支持可重用的流程片段,可通過XSLT和語義驗證轉換為BPEL;
- iProcess套件使用了事件驅動架構,包含一個強大的、向導式的BAM層,可對流程進行深入的檢視;
- 對很多標準有很好的支持,包括XSLT\XPDL\BPEL\BPMN等;流程可以保存為XPDL、可以很輕松的從BPMN轉換為運行時BPEL,和其他的BPM工具有互操作性,例如IDS Scheer;
- Business Studio設計仿真是高度圖形化的。他利用歷史改變數據、允許并行的比較設計。
- 流程改進的整個周期是不完整的。與SOA的整合、與開發者的整合尚不完整。因此,完成人工交互流、消息流和服務編排的開發過程較復雜。因為角色和階段的分離,導致往返工程較困難;
- Tibco產品“久經世故”,價格高昂,不易對規模較小或不成熟的組織產生吸引力;
- 對一些復雜內容交互的流程支持較少,比如說case-management-style的流程。
?
Cordys 從最初定位于應用平臺中間件,目前正擴張到BPMS陣營。C3為近期最新發布的BPMS,在很多方面得到顯著增強,例如BPM建模和執行,平臺與集成支持,安全與治理,還有案例管理。該廠商未包含在此報告中,是因為報告數據搜集時沒有趕上其最新產品發布的時機。
更多文章、技術交流、商務合作、聯系博主
微信掃碼或搜索:z360901061

微信掃一掃加我為好友
QQ號聯系: 360901061
您的支持是博主寫作最大的動力,如果您喜歡我的文章,感覺我的文章對您有幫助,請用微信掃描下面二維碼支持博主2元、5元、10元、20元等您想捐的金額吧,狠狠點擊下面給點支持吧,站長非常感激您!手機微信長按不能支付解決辦法:請將微信支付二維碼保存到相冊,切換到微信,然后點擊微信右上角掃一掃功能,選擇支付二維碼完成支付。
【本文對您有幫助就好】元