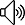二叉樹概念總結
1、二叉樹的遞歸定義
二叉樹(Binary Tree)是個有限元素的集合,該集合或者為空、或者由一個稱為根(root)的元素及兩個不相交的、被分別稱為左子樹和右子樹的二叉樹組成。
當集合為空時,稱該二叉樹為空二叉樹。在二叉樹中,一個元素也稱作一個結點。二叉樹是有序的,即若將其左、右子樹顛倒,就成為另一棵不同的二叉樹。即使樹中結點只有一棵子樹,也要區分它是左子樹還是右子樹。(二叉樹有五種形態)
2、二叉樹的相關概念
(1)結點的度。結點所擁有的子樹的個數稱為該結點的度。
(2)葉結點。度為0 的結點稱為葉結點,或者稱為終端結點。
(3)分枝結點。度不為0 的結點稱為分支結點,或者稱為非終端結點。
(4)左孩子、右孩子、雙親。樹中一個結點的子樹的根結點稱為這個結點的孩子。這個結點稱為它孩子結點的雙親。具有同一個雙親的孩子結點互稱為兄弟。
(5)路徑、路徑長度。如果一棵樹的一串結點n1,n2,…,nk有如下關系:結點ni是ni+1的父結點(1≤i<k),就把n1,n2,…,nk稱為一條由n1至nk的路徑。這條路徑的長度是k-1。
(6)祖先、子孫。在樹中,如果有一條路徑從結點M 到結點N,那么M 就稱為N的祖先,而N 稱為M 的孫。
(7)結點的層數。規定樹的根結點的層數為1,其余結點的層數等于它的雙親結點的層數加1。
(8)樹的深度。樹中所有結點的最大層數稱為樹的深度。
(9)樹的度。樹中各結點度的最大值稱為該樹的度。
3、二叉樹的主要性質
性質1: 在二叉樹的第i層上至多有2的i-1次方個結點(i>=1)。
性質2: 深度為k的二叉樹至多有2的k次方減1個結點(k>=1)。
性質3: 對任何一棵二叉樹T,如果其終端結點數為n0,度為2的結點數為n2,則n0=n2+1。
性質4: 具有n個結點的完全二叉樹的深度為|log2n|+1
性質5: 如果對一棵有n個結點的完全二叉樹的結點按層序編號,則對任一結點i(1≤i≤n)有:
(1) 如果i=1,則結點i是二叉樹的根,無雙親;如果i>1,則雙親PARENT(i)是結點i/2
(2) 如果2i>n,則結點i無左孩子(結點i為葉子結點);否則其左孩子LCHILD(i)是結點2i
(3) 如果2i+1>n,則結點i無右孩子;否則其右孩子RCHILD(i)是結點2i+1?
?
圖片來源: http://sunlei.blog.51cto.com/525111/111063
?二叉樹實現
?
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
class BinaryTreeNode {
int data;
BinaryTreeNode leftchild;
BinaryTreeNode rightchild;
BinaryTreeNode(int t) {
this.data = t;
this.leftchild = null;
this.rightchild = null;
}
BinaryTreeNode(int t, BinaryTreeNode leftchild, BinaryTreeNode rightchild) {
this.data = t;
this.leftchild = leftchild;
this.rightchild = rightchild;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
BinaryTreeNode root = null;
public BinaryTree(int[] t) {
creatBinaryTree(t);
}
/* 拷貝構造函數 */
public BinaryTree(BinaryTree otherTree) {
if (otherTree.root == null)
this.root = null;
else{
this.root=copy(otherTree.root);
//this.root=otherTree.root;
}
}
private BinaryTreeNode creatBinaryTree(int[] t) {
int length = t.length;
if (root == null) {
root = new BinaryTreeNode(t[0]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
creat(root, t[i]);
}
return root;
}
// 構造二叉樹
private void creat(BinaryTreeNode root, int t) {
if (t >= root.data) {
if (root.rightchild == null) {
root.rightchild = new BinaryTreeNode(t);
} else {
creat(root.rightchild, t);
}
} else {
if (root.leftchild == null) {
root.leftchild = new BinaryTreeNode(t);
} else {
creat(root.leftchild, t);
}
}
}
/* 遍歷二叉樹 前中后*/
public void inIterator(BinaryTreeNode b) {
if (b != null) {
inIterator(b.leftchild);
System.out.print(b.data + ",");
inIterator(b.rightchild);
}
}
public void levelOrderDisplay(BinaryTreeNode b){
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<BinaryTreeNode> q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<BinaryTreeNode>();//創建鏈式隊列對象
if(b == null)return;
BinaryTreeNode curr;
q.add(b); //根結點入隊列
while(!q.isEmpty()){ //當隊列非空時循環
curr = (BinaryTreeNode)q.remove(); //出隊列
System.out.println(curr.data); //訪問該結點
if(curr.leftchild != null)
q.add(curr.leftchild); //左孩子結點入隊列
if(curr.rightchild != null)
q.add(curr.rightchild);//右孩子結點入隊列
}
}
/* 樹的高度 */
public int treeHeight(BinaryTreeNode b) {
if (b == null)
return -1;
else
return (treeHeight(b.leftchild) >= treeHeight(b.rightchild) ? treeHeight(b.leftchild)
: treeHeight(b.rightchild)) + 1;
}
/* 求總節點數 */
public int treeNodes(BinaryTreeNode b) {
if (b == null)
return 0;
else if (b.leftchild == null && b.rightchild == null)
return 1;
else
return 1 + treeNodes(b.rightchild) + treeNodes(b.leftchild);
}
/* 求葉節點數 */
public int treeLeavesNode(BinaryTreeNode b) {
if (b == null)
return 0;
else if (b.leftchild == null && b.rightchild == null)
return 1;
else
return treeLeavesNode(b.rightchild) + treeLeavesNode(b.leftchild);
}
/* 復制樹 */
public BinaryTreeNode copy(BinaryTreeNode b) {
BinaryTreeNode newNode;
if (b == null)
return null;
newNode=new BinaryTreeNode(b.data);
newNode.leftchild = copy(b.leftchild);
newNode.rightchild = copy(b.rightchild);
//newNode = new BinaryTreeNode(b.data, newLeftChild, newRightChild);
return newNode;
}
/*刪除樹*/
public void delete(){
deleteTree(this.root);
System.out.println(this.root.rightchild.rightchild.rightchild==null);
}
public void deleteTree(BinaryTreeNode b){
if(b!=null){
deleteTree(b.leftchild);
deleteTree(b.rightchild);
b=null;
}
}
/* 查找一個節點 */
public boolean findNode(BinaryTreeNode b,int key){
if(b==null)return false;
if(b.data==key)return true;
if(key>b.data)return findNode(b.rightchild,key);
return findNode(b.leftchild,key);
}
public void insertNode(BinaryTreeNode b,int t){
creat(b,t);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = { 12, 11, 34, 45, 67, 38, 56, 43, 22, 8};
System.out.println(data.length);
BinaryTree btree = new BinaryTree(data);
BinaryTreeNode r = btree.root;
btree.inIterator(r);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Height:" + btree.treeHeight(r));
System.out.println("Nodes:" + btree.treeNodes(r));
System.out.println("Leaves:" + btree.treeLeavesNode(r));
BinaryTree copyTree=new BinaryTree(btree);
System.out.println("copyTree:");
copyTree.insertNode(copyTree.root, 57);
System.out.println("Height:" + copyTree.treeHeight(copyTree.root));
System.out.println("Nodes:" + copyTree.treeNodes(copyTree.root));
System.out.println("Leaves:" + copyTree.treeLeavesNode(copyTree.root));
System.out.println("Btree Height:" + btree.treeHeight(r));
System.out.println("Nodes:" + btree.treeNodes(r));
System.out.println("Leaves:" + btree.treeLeavesNode(r));
System.out.println(copyTree.findNode(copyTree.root, 8));
copyTree.inIterator(copyTree.root);
/* copyTree.delete();
System.out.println(copyTree.root==null);
System.out.println("deleteTree:");
System.out.println("Height:" + copyTree.treeHeight(copyTree.root));
System.out.println("Nodes:" + copyTree.treeNodes(copyTree.root));*/
System.out.println("LevelOrder:");
copyTree.levelOrderDisplay(copyTree.root);
}
}
?
更多文章、技術交流、商務合作、聯系博主
微信掃碼或搜索:z360901061

微信掃一掃加我為好友
QQ號聯系: 360901061
您的支持是博主寫作最大的動力,如果您喜歡我的文章,感覺我的文章對您有幫助,請用微信掃描下面二維碼支持博主2元、5元、10元、20元等您想捐的金額吧,狠狠點擊下面給點支持吧,站長非常感激您!手機微信長按不能支付解決辦法:請將微信支付二維碼保存到相冊,切換到微信,然后點擊微信右上角掃一掃功能,選擇支付二維碼完成支付。
【本文對您有幫助就好】元